About Cognitive Behavior Therapy
Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT) is a time-sensitive, structured, present-oriented psychotherapy that has been found to be effective in more than 2,000 studies for the treatment of many different health and mental health conditions. CBT is based on Dr. Aaron T. Beck’s Cognitive Model, which is the theory that the way individuals perceive a situation is more closely connected to their reaction than the situation itself.
In CBT treatment, trained therapists help clients identify distressing thoughts and evaluate how realistic these thoughts are. As clients become aware of their thoughts and are able to evaluate them, they feel better. CBT therapists also work with clients on solving problems, learning new skills, and setting and achieving meaningful goals. Although initially therapists and clients work together in session, therapists also empower clients by teaching them to evaluate their thoughts and practice their new skills on their own, outside of therapy.
At Beck Institute, we practice and teach a contemporary approach to CBT that emphasizes clients’ strengths and values. We prioritize a strong therapeutic relationship and deliver holistic treatment that is appropriately adapted to each client’s background, culture, experiences, and preferences.
Cognitive Model
The cognitive model describes how people’s thoughts and perceptions influence the way they feel and behave. The cognitive model is at the core of CBT, and it plays a critical role in helping therapists conceptualize and treat their clients’ difficulties.
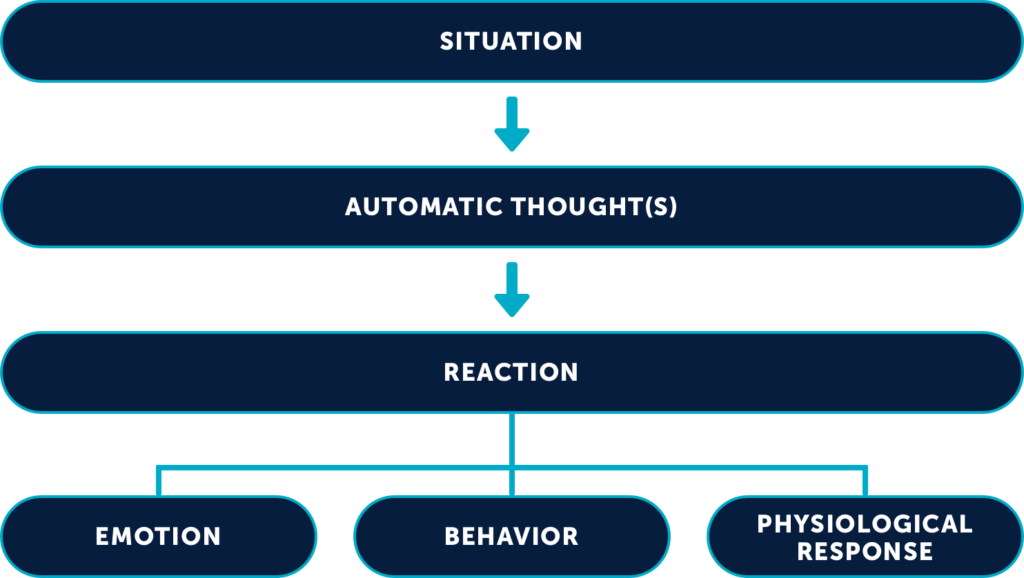
Principles of Treatment
CBT therapists use an individual formulation to guide treatment for each client. This formulation is essential to developing a sound therapeutic relationship, setting goals, planning treatment, and selecting interventions.
Fourteen tenets of good CBT:
- CBT treatment plans are based on an ever-evolving cognitive conceptualization.
- CBT requires a sound therapeutic relationship.
- CBT continually monitors client progress.
- CBT is culturally adapted and tailors treatment to the individual.
- CBT emphasizes the positive.
- CBT stresses collaboration and active participation.
- CBT is aspirational, values based, and goal oriented.
- CBT initially emphasizes the present.
- CBT is educative.
- CBT is time sensitive.
- CBT sessions are structured.
- CBT uses guided discovery and teaches clients to respond to their dysfunctional cognitions.
- CBT includes action plans (therapy homework).
- CBT uses a variety of techniques to change thinking, mood, and behavior.
© 2018. Adapted from J. Beck (2020) Cognitive Behavior Therapy: Basics and Beyond, 3rd edition
CBT Assessment Tools
There are a variety of helpful CBT tools to help mental health practitioners in their work with patients, including the Beck Depression Scale, the Beck Hopelessness Scale, the Personality Belief Questionnaire, and more.
Research
People often ask, ‘Does CBT work?’ The answer is clear: yes. More than 2,000 studies have demonstrated the efficacy of CBT for psychiatric disorders, psychological problems and medical problems with a psychiatric component.
Get Trained in CBT
Our trainings include live virtual workshops, on-demand online courses, webinars, and more.